
Customers don’t just make purchases—they seek reliability, personalized solutions, and meaningful connections. According to Gartner predicting that 80% of B2B sales interactions will occur in digital channels, the need for a human touch in sales has never been greater. While automation and AI can streamline processes, they can’t replace the deep connections that personal selling fosters.
Personal selling allows businesses to build trust, address pain points directly, and deliver tailored solutions that resonate with buyers. In an increasingly digital world, human interaction remains a key differentiator, turning potential transactions into long-term partnerships that drive business success and customer loyalty.
Table of Contents:
- What is Personal Selling?
- Personal Selling Importance
- Types of Personal Selling
- 7 Stages of the Personal Selling Process
- Effective Personal Selling Strategies
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Personal Selling
- Conclusion
- Personal Selling Frequently Ask Questions (FAQs)
What is Personal Selling?
Personal selling involves direct interaction between a salesperson and a potential buyer. It is commonly used in B2B sales, retail, and trade selling, where developing strong relationships and building trust are crucial. Compare this to mass marketing, where with personal selling, you have real-time communication with potential customers. This enables sales individuals to overcome objections, clear doubts, and tailor their pitch according to buyer reactions. One of the main advantages of personal selling is the ability to build long-term relationships.
Salespeople gain a comprehensive understanding of their customers’ pain points across dozens of touchpoints, including in-person meetings, video calls, phone conversations, and emails. This personalized mechanism improves the customer experience and increases the chances of conversion.
Customers with high-ticket or complex products can significantly benefit from personal selling because they often need in-depth explanations and reassurance before buying. However, any company can use personal interactions to differentiate itself in an age of automated sales pitches. Ultimately, customers remember the sales professional who gave them real value for long-term loyalty, not the chatbot retrieving information.
Personal Selling Importance
Personal selling remains a powerful tool that adds immense value to the customer journey. Unlike automated digital interactions, personal selling fosters meaningful relationships, provides tailored solutions, and enhances sales effectiveness. Here are some key benefits and how it transforms the buyer’s experience.
1. Builds Strong Relationships
B2B sales success depends significantly on long-term relationships. Businesses do not rely on transactional business, one-time sales, which could have been made online. Personal selling allows sales representatives to develop rapport and build trust with their customers, presenting themselves as experts cross-functional to an organization rather than just a faceless vendor.
For example, a B2B customer buying a SaaS solution might require continuous system integration, troubleshooting, and upscaling. A committed salesperson who checks in regularly and offers solutions helps create a partnership and ensures that the customer will be more likely to remain.
2. Allows Customization
Every business has its own set of needs and challenges. One major reason is that personal selling allows sales reps to tailor their pitches according to individual customer pain points. Such an approach ensures that customers get solutions that are aligned with their business goals.
Imagine a manufacturing company that needs supply chain optimization software. A good salesperson wouldn’t simply demonstrate functionality; they would examine the business’s function process, determine inefficiencies, and recommend how the software might solve those problems. This degree of authority makes shoppers feel valued and knowledgeable.
3. Facilitates Complex Sales
B2B transactions usually involve many decision-makers, extended sales cycles, and detailed contract discussions. Personal selling can help with these complexities, allowing for clear communication, real-time answers to concerns, and alignment for all stakeholders involved.
For instance, selling enterprise-level cybersecurity software requires convincing IT teams, compliance officers, and financial decision-makers. Since a personal selling approach accommodates all stakeholders, the sales rep can adjust his communication expediently, giving way to a smooth and informed decision-making process.
4. Increases Sales Effectiveness
Research shows that businesses leveraging personal selling experience have up to a 40% higher close rate than those relying solely on digital methods. Why? If you are talking to someone in person, you can persuade them directly, overcome their objections on the fly, and bring your proposition to life.
A sales professional conducting in-person or video meetings can gauge a prospect’s interest, adjust their messaging, and reinforce key selling points based on the customer’s reactions. This flexibility leads to more successful conversions.
5. Provides Immediate Feedback
Unlike email marketing or automated sales funnels, personal selling allows for real-time feedback. Sales representatives can immediately meet objections, clarify doubts, and tweak their approach, which makes for a smooth sales process.
Imagine that a prospect asks you about the price but seems doubtful. Rather than waiting for an email response, a sales representative can respond on the spot, suggesting different pricing tiers or demonstrating ROI calculations to justify the purchase. These proactive engagements help to close the deals faster.
Supercharge Your Sales with Actionable Insights!
Transform your sales growth with PrimeRole verified data and AI-enriched company insights
Types of Personal Selling
Personal selling is an important component of your sales strategy, and involves direct interaction between sales representatives and customers.
Different types of personal selling are used by businesses as per their requirements and the manner they market approach. Here are three main types include:
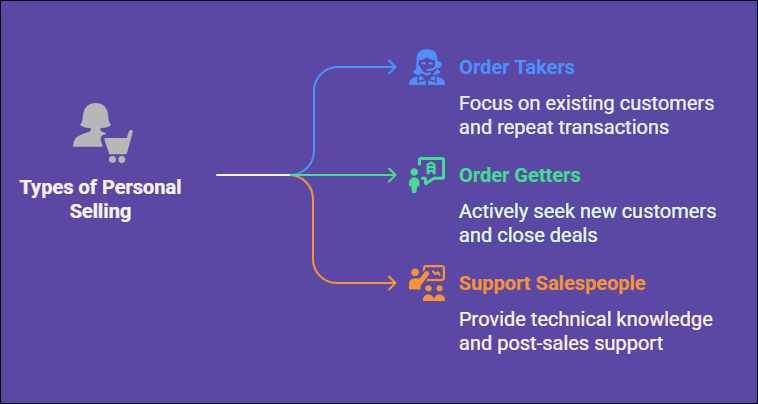
1. Order Takers
Order takers are more concerned with the existing customers they deal with and the transactions they complete than they do pursuing new leads. They answer customer queries, place repeat orders, maintain relationships, and complete the sales process.
2. Order Getters
Unlike order takers, order getters actively seek out new customers, generate leads, and persuade prospects to make a purchase. They are responsible for business growth by identifying opportunities, closing deals, creating presentations, product demonstrations, and negotiations.
3. Support Salespeople
Support salespeople who can help sell by being a technical knowledgeable salesperson, training, and post-sales support. This is a critical role for industries that demand a more robust understanding of products, like tech, health, or industrial equipment.
7 Stages of the Personal Selling Process
Selling isn’t just about luck—it’s a structured process that, when followed correctly, increases your chances of success. Every step helps guide potential customers toward making a purchase while ensuring their needs are met. Let’s break down the seven stages of the personal selling process.
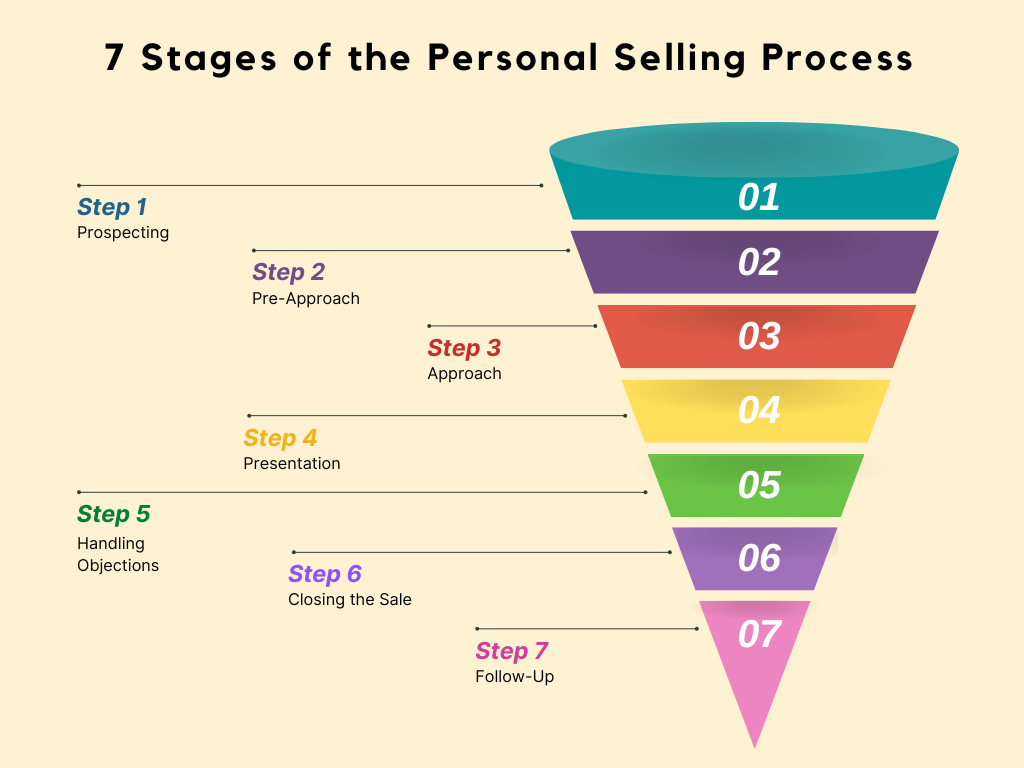
1. Prospecting – Finding the Right Customers
The first step in personal selling is identifying potential customers who may benefit from your product or service. This is called prospecting. It involves lead generation through various methods such as:
- Cold calling – Reaching out to potential clients who haven’t interacted with your business before.
- Networking – Building relationships through events, LinkedIn, or referrals.
- Social media – Engaging with prospects on platforms like Twitter and Instagram.
- Inbound marketing – Using blogs, videos, or email campaigns to attract interested buyers.
Not every lead is a good fit, so lead qualification is essential. Before reaching out, research whether a prospect has the need, budget, and decision-making power to purchase.
Qualify High-Value Prospects Instantly
Optimize lead scoring with PrimeRole’s AI-driven ICP qualification system
2. Pre-Approach – Doing Your Homework
It's crucial to prepare before you make the first contact. The pre-approach phase involves researching your prospects to understand their pain points, interests, and buying behavior. Here are some key aspects to consider during this phase.
- Identifying the business, industry or personal needs.
- Knowing what solutions they might already have.
- Determining some ways the value provided by your product or service is better.
With this data, you can tailor your sales pitch to be more applicable and attractive to the prospect.
3. Approach – Making a Strong First Impression
This approach involves direct interaction with the prospect. The goals of this process are to build relationships and rapport with potential customers by making direct phone calls, emails, and in-person meetings.
A great approach includes:
- A warm greeting that makes the prospect feel comfortable.
- An engaging introduction that highlights why you’re reaching out.
- Asking insightful questions to understand their specific needs.
This stage is not about selling immediately—it’s about opening the conversation and establishing rapport.
4. Presentation – Showcasing Your Solution
In this stage, businesses present their products and services to potential customers. This is where you emphasize how your solution addresses the prospect's pain points. Here are some key elements of an effective presentation:
- Tailor your presentation to the customer’s needs based on your earlier research.
- Use visuals, product demonstrations, or real-world examples to clearly communicate the benefits.
- Focus on how your offering improves their life or business.
Instead of merely listing features, illustrate how your product makes things easier, faster, or more cost-effective for them.
5. Handling Objections – Overcoming Concerns
Not all prospects are going to say, “Yes, I’m in” immediately. They may have concerns around price, functionality, or competitor offerings.
Here are Common objections include:
- “It’s too expensive.” → Highlight the long-term value and ROI.
- “I’m happy with my current solution.” → Show what makes yours unique.
- “I need more time to decide.” → Offer additional support or a trial.
Instead of arguing, listen carefully, acknowledge their concerns, and respond with well-prepared, reassuring answers.
6. Closing the Sale – Sealing the Deal
The closing stage is crucial for encouraging the prospect to make a decision. This may involve presenting incentives or time-limited offers that create a sense of urgency and addressing any last-minute concerns they might have.
Closing techniques can vary greatly. Some salespeople use urgency-driven approaches, such as offering one-time discounts, while others might use the assumptive close, in which the conversation is framed as if the deal has already been agreed to.
It does not matter which way you believe is best, but whatever you choose, remember that the key is ensuring the prospect leaves feeling confident and excited about their purchase.
7. Follow-Up – Building Long-Term Relationships
Many salespeople stop at closing, but the real magic happens in the follow-up. After the sale, check in with the customer to:
- Ensure they’re satisfied with their purchase.
- Offer additional support or resources.
- Ask for referrals or reviews.
A great follow-up strengthens relationships and increases the likelihood of repeat business. Customers who feel valued are more likely to return and recommend your brand to others.
Effective Personal Selling Strategies
Personal selling is more than just making a pitch—it’s about understanding customer needs, building trust, and delivering solutions that create value. Mastering key strategies can significantly improve your sales effectiveness, whether you’re selling a product, service, or idea. Below are six essential personal selling strategies to enhance your approach and close more deals.
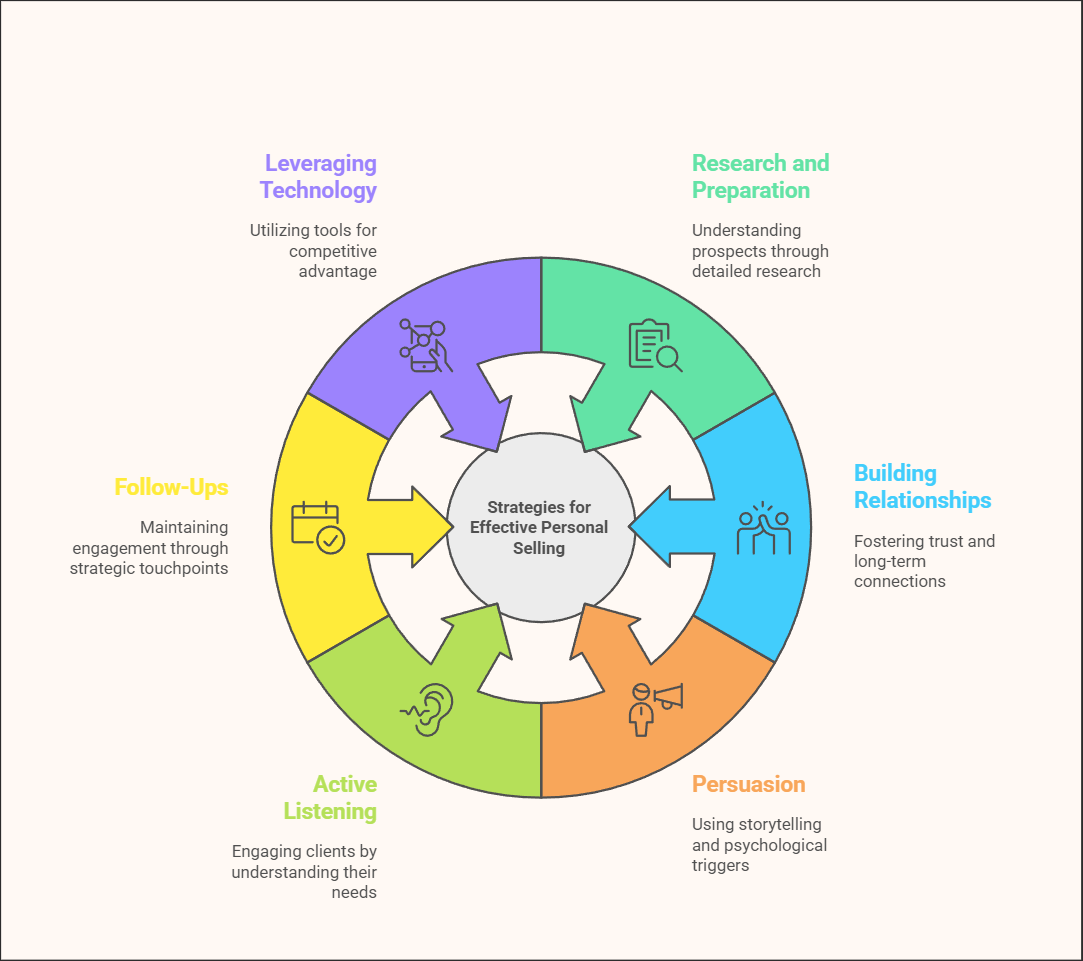
1. Research and Preparation
Effective selling starts with thorough research. Understanding a prospect’s industry, challenges, competitors, and decision-making hierarchy is crucial. Conducting in-depth research allows sales professionals to tailor their approach, anticipate objections, and provide relevant solutions. Leveraging industry reports, analyzing company financials, and tracking recent developments help in crafting a well-informed pitch that resonates with the prospect’s specific needs.
2. Build Strong Relationships
Trust and networking are key components of B2B sales. They create a long-term relationship with the customer. Fostering trust through tailored interaction, timely follow-ups, and value-added conversations forms the foundation of successful business relationships. Sales professionals can earn trust as advisors, not vendors, by being open and familiar with the customer's pain points.
3. Master the Art of Persuasion
Compelling storytelling, use cases, and a customized solution value proposition help you stand out. Convincing people in sales requires knowing psychological triggers, listening to pain points, and presenting solutions that fit in with their strategic objectives. Showcasing real-life successes, incorporating social proof, and showcasing ROI add to a compelling argument for your service.
4. Active Listening and Problem-Solving
Understanding the customer’s problems is essential so that you can align your solution to their requirements. Active listening involves asking open questions, recognizing pain points, and providing strategic advice that addresses those pain points. Focusing on problem solving rather than shipping a product and simply being a sales professional builds a better rapport and supplies you with a customized problem solution that generates value for your customer.
5. Effective Follow-Ups
Closing a deal may take several touchpoints. By staying in touch through planned follow-up communications, you can keep prospects engaged while reminding them why they were initially interested. Personalized follow-up emails, checking in with helpful insights, or considerate touchpoints like relevant case studies or articles go a long way to show you care. Proven follow-up techniques help lead nurturing, objection handling, and lead conversion.
6. Leveraging Technology
Sales intelligence tools provide sales professionals with a competitive advantage when they become part of their workflow. PrimeRole, an AI-powered sales intelligence platform, offers sale-read data, AI-enriched insights, and real-time signals to sales teams to discover high-potential prospects and close deals faster.
With PrimeRole’s multi-provider waterfall enrichment, sales teams have the most accurate and up-to-date contact and company data for every one of their new opportunities, guaranteeing they always reach the right decision-makers. Its sophisticated verification system solves the problem of insufficient data by validating emails, verifying phone ownership, and scoring confidence levels with information from multiple sources.

In addition, PrimeRole’s AI-powered Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) matching utilizes web signals and real-time behaviors to identify the best-fit prospects for sales professionals effortlessly. The platform’s seamless CRM integration and real-time updates create ready-to-go enhanced insights, whether a CRM, data lake, or engagement tool.
Built with advanced sales intelligence functionalities, PrimeRole empowers businesses with precise lead targeting, sales productivity, and conversion optimization, minimizing guesswork from prospecting.
AI-Powered Lead Generation for Faster Growth
Automate outreach, personalize engagement, and boost conversions effortlessly with PrimeRole.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Personal Selling
Deciding whether to incorporate personal selling into your b2b sales strategy requires a deep understanding of its pros and cons. While it offers businesses a powerful tool to build relationships and close high-value deals, it also comes with challenges. Below is a comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of personal selling:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Builds strong relationships: Personalized approach builds trust and encourages long-term partnerships. | Time-consuming: Personal selling requires significant time investment compared to digital sales methods. |
| Highly customizable: Sales pitches can be customized to each prospect’s specific needs. | Expensive: Hiring, training, and maintaining a sales force can be costly. |
| Effective for complex sales: Ideal for B2B deals that involve multiple decision-makers and lengthy negotiations. | Scalability issues: Difficult to reach a large audience simultaneously compared to digital marketing. |
| Immediate feedback: Sales reps can address concerns and objections in real time. | Relies on salesperson’s skill: The success of personal selling depends heavily on the abilities of the sales representative. |
| Higher conversion rates: One-on-one interactions often lead to better sales outcomes. | Geographical limitations: Personal selling requires travel and in-person meetings, which may not always be feasible. |
Conclusion
Personal selling is a hands-on sales approach that works best when businesses need to connect with clients on an individual level to build trust and provide tailored solutions. While it requires time and effort, it remains one of the most effective ways to close high-value B2B deals and establish long-term relationships.
If you’re looking for a platform to enhance your personal selling strategy, consider Primerole. This innovative solution helps businesses streamline their sales efforts, manage client interactions, and optimize customer engagement.
By integrating personal selling with digital tools, businesses can achieve a perfect balance between human connection and efficiency.
Personal Selling Frequently Ask Questions (FAQs)
What is the meaning of personal selling?
Personal selling is a direct, in-person sales technique where a salesperson engages with potential buyers to assess their specific needs, address concerns, and deliver personalized solutions. This approach fosters trust, builds strong business relationships, and allows for real-time feedback, making it particularly valuable in B2B sales scenarios where decision-making is complex and requires tailored interactions.
What are the main types of personal selling?
The three main types are order takers (who process existing customers’ orders), order getters (who actively seek new customers), and support salespeople (who provide technical assistance and post-sales service).
What are the examples of personal selling?
Personal selling examples include real estate agents negotiating property deals, pharmaceutical reps educating doctors on new medications, and B2B sales professionals offering customized software solutions to enterprises. Other examples include car salespeople providing tailored financing options and financial advisors helping clients choose investment plans based on their goals.
